
Earth and atmospheric sciences provide us with an understanding of the Earth’s origin, history, structure and global processes. Through these, we know of the hazards associated with the dynamic phenomena of the Earth, and this knowledge enables us to take steps to minimize the losses to our lives and to our life support systems
The biological sciences provide us with a greater understanding of life on earth. Medical sciences enable us to deal with diseases and disorders in humans and animals. These two closely connected fields are presently going through a major transition that may be regarded as a scientific revolution. Developments in these branches will considerably influence life on this planet.

Food is one of the basic needs in life. The production, distribution and the nutritional quality of food are key elements of life support systems. The achievement of sustainable world food security, which has long been a noble goal of the development community, depends on strengthening these systems.

Mathematics helps produce better models that make better predictions and then the policy makers should use those models. Properly used, mathematical models can be very valuable supports for policy analysis and associated decision making.

Physical sciences are essential knowledge resources in our increasingly technical world. Much of modern technology is the result of physics research, including the transistor, and integrated circuits, which are at the heart of modern computers and electronics.

Life on Earth arose and evolved around water, and, even though much of the natural world later became terrestrial, the dependence of life on water always has been, and always will be, absolute. Biodiversity cannot survive without water, and neither can humanity.

The topsoil is a micro-ecosystem composed of living and dead organic parts, and inorganic parts derived from rocks, the water cycle, and the atmosphere. Only by recognizing the fundamental importance of soils we can foster an incentive for their conservation or improvement, for the benefit of present and future generations.

Traditionally, development economics has been concerned with economic growth and economic transformation, and often without considering social, political, and cultural aspects of society that influence economic behavior. Traditional economics has been found to be inadequate because it fails to correct social inequity or to guarantee sustainability.

Development is not about human development or sustainable development alone, but about ‘sustainable human development’. Sustainable human development is quite strongly associated with, and is ultimately a means of developing, sustainable human capital as an important component of the wealth of a nation.

Equity within generations and across generations is an important requirement for sustainable development

A culture of Peace with positive peace, not just a state in which wars, conflicts, and violence are prevented by pressures, is key to sustainable development.
Social Sciences and Humanities in the global Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS), which is an integrated compendium of twenty one Encyclopedias
Biotechnology is a technology using biological systems and parts thereof for the benefit of humankind. Biotechnology draws on the pure biological sciences and in many instances is also dependent on knowledge and methods from outside the sphere of biology.

Understanding the value of biological diversity and ecosystem health enhances our true wealth in terms of products and services provided by the ecosystems around us.

The provision of reliable and convenient energy supplies has been a high priority issue for all nations, and success in this field has been an important factor in reducing poverty and in shaping social development.

Chemical sciences should play a very positive role in sustainable development, contributing to improvement in quality of life for present and future generations. But, without control, human made chemicals have the potential to create enormous negative impacts. We need further development of chemical sciences; but we also need enlightened management of the science to ensure that the effects are beneficial to humanity.

Tropical environments cover the most part of still preserved natural areas of the Earth. The greatest biodiversity, as in terms of animals and plants, as microorganisms, is placed in these hot and rainy ecosystems spread up and below the Equator line. Additionally, the most part of food products, with vegetal or animal origin, that sustain nowadays human beings is direct or undirected dependent of tropical productivity.
The Earth’s non-renewable resources of energy, particularly oil and gas, are being depleted at a rapid rate and there is little indication that research and development of renewable energy sources is progressing fast enough to permit an orderly transition to a sustainable energy future.

Technology, Information, and Systems Management Resources have potential applications in support of sustainable development. They add new dimensions to human ability and expand the range of opportunities in the process.

In almost all technical fields spectacular human achievements have been rendered possible only because of the progress of control technology. Together with computer and information technologies, control engineering represents one of the key technologies of the future.
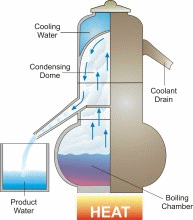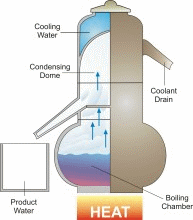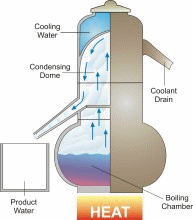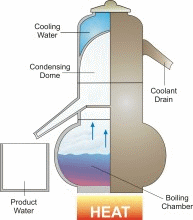
DESWARE focusing on the specific topics of desalination and water resources. Desalination has already made a major contribution to quality of life in the most arid regions of the world. Without desalination, many of these regions would have remained uninhabited.